A common way to classify gearmotors is by the output shaft orientation, and two of the standard types are parallel and right-angle arrangements. Beyond shaft configuration itself, other factors such as the type of gears used in the gearmotor determine performance.

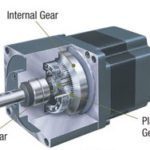
Generally speaking, a right-angle gearmotor is less efficient than a parallel configuration. A typical right-angle gearmotor arrangement includes a worm gear assembly, which serves to translate the rotary motion of the motor by 90 degrees. In parallel-shaft gearmotors, the gear setup can take any number of forms, from helical and spur gears to complex planetary gear systems. In terms of gear efficiency, spiral bevel gears tend to have the greatest efficiency, followed closely by helical and spur gear types, all of which are in the range of 93 to 99%.
More demand for compact machine designs means that space considerations are an important design priority. So if your application calls for a right-angle gearmotor as the only one that will fit the design requirements without having to redesign the entire machine, then that’s the one you go with. Even if it sacrifices some efficiency, compactness and fit may be the more relevant design factors.




Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.