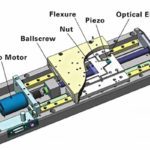
Piezo motors are known for their extremely small size and high size-to-torque ratio, as well as high-resolution movements (micrometer and even nanometer-level resolution.) The high resolution is attributable to the inherent design of piezo motors themselves, but feedback also helps to ensure highly accurate movement on the order of nanometers.

As a general rule, piezo motors can be operated either open loop or closed loop. The advantage of closed-loop operation is that it offers higher precision and greater repeatability and linearity. Closed-loop feedback also helps eliminate drift and hysteresis, both factors that can negatively impact precision and accuracy.
There are a few common types of feedback used with piezo motors ranging from strain gauges to optical encoders, depending on the application requirements:
-
-
- Optical encoders: Incremental optical encoders are commonly used for piezo motor feedback. However, absolute encoders can be used as well, although they are typically more costly than incremental encoders.
- Capacitive sensors: Along with strain-gauge sensors, these are the most common as they are relatively inexpensive, compact, and provide good quality nanometer-resolution readings.
- Laser interferometers: These offer sub-nanometer resolution, but they are also more bulky and expensive than either capacitive based sensors or encoders.
-




Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.